 Gout
is a group of disorders of purine metabolism which causes an excess of serum
uric acid. Deposition of urate occurs in articular or extra-articular tissues.
This excess of uric acid can be caused by over-production or under-excretion
by the body. In both these types of patients, excessive intake of foods containing
purines can contribute to hyperuricemia. Men are affected more often than
women.
Gout
is a group of disorders of purine metabolism which causes an excess of serum
uric acid. Deposition of urate occurs in articular or extra-articular tissues.
This excess of uric acid can be caused by over-production or under-excretion
by the body. In both these types of patients, excessive intake of foods containing
purines can contribute to hyperuricemia. Men are affected more often than
women.
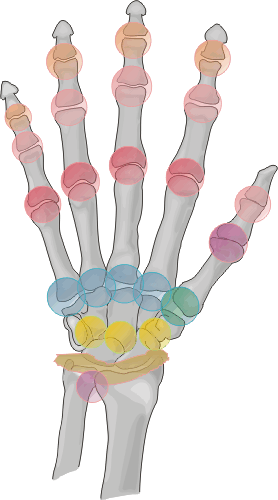
Distribution:
While all of the compartments of the hand and wrist are susceptible, the carpometacarpal
and intercarpal joints are the most frequently involved. Asymmetric distribution
is characteristic of gouty arthritis.
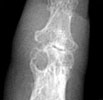
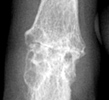
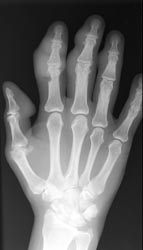
Radiographic Appearance:
Periarticular soft tissue swelling may be the first radiographic sign of an
acute gouty attack. Soft tissue sodium urate deposits can occur with chronic
gout which creates a dense mass called a tophus that can occasionally contain
calcifications. This distribution is random and is usually seen on the dorsal
surfaces. Osseous erosions are periarticular with sharp sclerotic margins
and an asymmetric distribution. Overhanging edges with a well-defined osseous
shelf at the erosive site can sometimes be seen. Loss of normal bone mineralization
is not a characteristic finding of gout and if present, the osteoporotic findings
are mild. Joint space narrowing does not usually present except in more advanced
stages.
Differential Diagnosis:
Chronic gout may be mistaken for rheumatoid arthritis as the joint spaces
narrow. However, in rheumatoid arthritis, joint involvement is symmetric,
erosions do not have sclerotic margins, and juxta-articular osteoporosis may
be present. Osteoarthritis may also be mistaken for gout and can also occur
concurrently.