 Hemochromatosis
is an inherited disorder where there is increase in total iron body stores.
This leads to deposition of iron in parenchymal tissues, eventually causing
functional impairment. Men are affected far more frequently than in women.
Arthritic changes are seen in approximately half of the patients.
Hemochromatosis
is an inherited disorder where there is increase in total iron body stores.
This leads to deposition of iron in parenchymal tissues, eventually causing
functional impairment. Men are affected far more frequently than in women.
Arthritic changes are seen in approximately half of the patients.
Distribution:
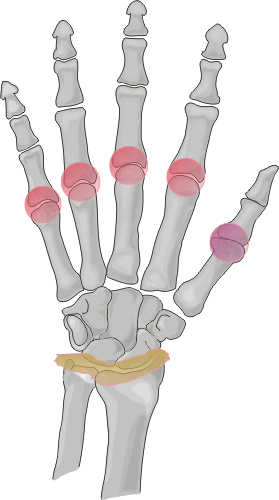
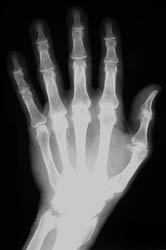
Commonly affected sites of the hands include the metacarpal heads, especially
at the 2nd and 3rd metacarpophalangeal joints, and the interphalangeal and
carpal joints. .
Radiographic Appearance:
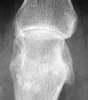
Osseous eburnation, joint space narowing, well-defined subchondral cysts,
radial beak-like osteophytosis at the metacarpal heads, and osteoporosis are
all radiographic findings which are frequently seen in this disease process.
Chondrocalcinosis is seen in up to fifty percent of the cases, with a direct
correlation noted between the amount of chondrocalcinosis and the degree of
arthropathy.
Differential Diagnosis:
Soft tissues findings in the skin and hand help differentiate psoriatic arthritis
from findings in hemochromatosis. There is more involvement of the distal
joints in the hands with osteoarthritis. It may be difficult to differentiate
hemochromatosis from rheumatoid arthritis based on radiographic findings;
however, osteophytosis is rarely seen in RA. Greater propensity for the MCP
joints with medial beak-like osteophytosis at the metacarpal heads and more
widespread involvement of the carpal bones may help to differentiate hemochromatosis
from idiopathic CPPD disease.