 Rheumatoid
Arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder with primary effects
on the synovial joints. Rheumatoid factor is present in approximately 80%
of patients with RA; these patients usually have more severe disease features.
Women are affected approximately 3 times more often than men.
Rheumatoid
Arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder with primary effects
on the synovial joints. Rheumatoid factor is present in approximately 80%
of patients with RA; these patients usually have more severe disease features.
Women are affected approximately 3 times more often than men.
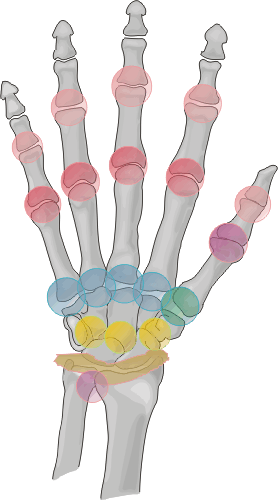
Distribution:
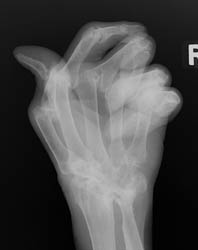
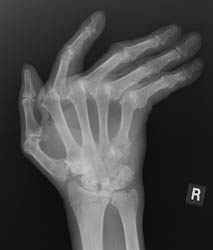
This disease is a bilaterally symmetrical and polyarticular process. Commonly
affected joints of the hand and wrist include the MCP, PIP, any of the wrist
joints, and the distal ulna and radial styloid. The distal interphalangeal
joints are rarely involved.
Radiographic Appearance:
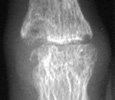
The earliest signs of the disease process are periarticular soft tissue swelling
due to effusion, tenosynovitis and edema. Joint spaces may actually widen
in the early stages of RA. Periarticular osteopenia can also be seen. Early
articular changes occur at the "bare area" of small joints, which
are not covered by cartilage. These marginal erosions are often first seen
at the 2nd and 3rd MCP and the 3rd PIP articulations.
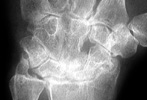
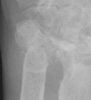
Advanced signs of RA include diffuse loss of joint space due to loss of cartilage. There can also be marginal or central erosions and severe joint deformities. Subluxations and dislocations may lead to ulnar deviation at the MCP joints and radial deviation at the radiocarpal articulations of the wrists. Erosive changes are also noted at the distal ulna and radial styloid. Joint deformities seen in RA include a Boutonniere deformity (flexion at the PIP joint and hyperextension at DIP joint) and a Swan-neck deformity (hyperextension at the PIP joint and flexion at the DIP joint). In severe cases, there may be radiographic findings of ankylosis at the proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints.
Differential Diagnosis:
The differential includes SLE and seronegative spondyloarthropathies such
as ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and Reiter's arthritis. The
DIP joints are often not affected in RA. Furthermore, the radiographic findings
of subchondral sclerosis and osteophytosis are often absent.