Arthrography
- Most frequently used for the evaluation of infection
- Confirms intra-articular position of needle
- Demonstrates abscess cavities, bursae, and sinus tracts
- Sensitivity for infection: 66-90%(Dussault, Teranzedeh)
- Limited sensitivity for loosening
- Done under fluoroscopic guidance
- Surgical scar examined for areas of leakage or dehiscence
- Femoral artery palpated and marked
- Needle entry site lateral to femoral artery, at level of groin crease,
orthogonal to neck of prosthesis
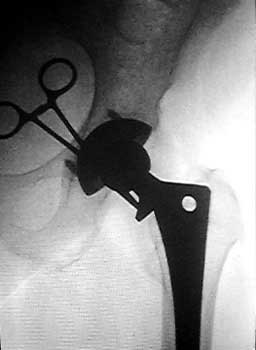
- Needle advanced to metal
- Standard sterile technique
- 20 gauge spinal needle
- Needle is felt striking metal. Attempt is made to place needle at edge of
prosthesis, so the tip can be as inferior as possible, where more fluid
collects.
- Joint fluid aspirated and sent for gram stain, aerobic and anaerobic cultures
and sensitivities, cell count and differential, labeled hip aspirate. Fungal and
AFB cultures sent if needed.
- Arthrogram performed with sequential digital subtracted spot films, 1 every 2
seconds, during contrast injection.
- Contrast aspirated and sent for cultures labeled hip wash.
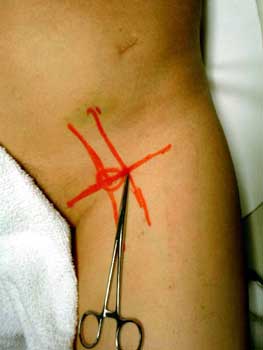 
Femoral artery marked. Forceps at area of planned needle
insertion
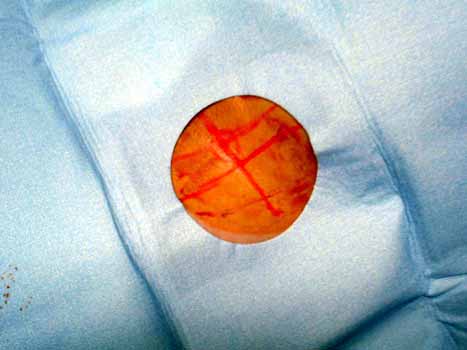
Sterile prep and drape
ARTHROGRAPHY
Needle advanced to metal
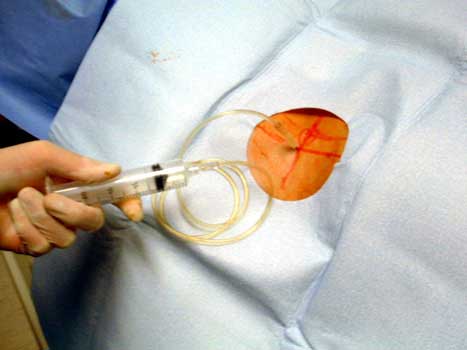
Aspiration of joint fluid
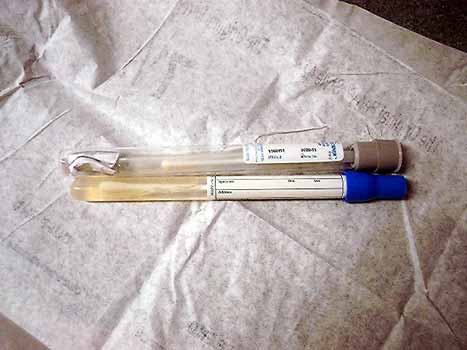
Aerobic and anaerobic culture tubes
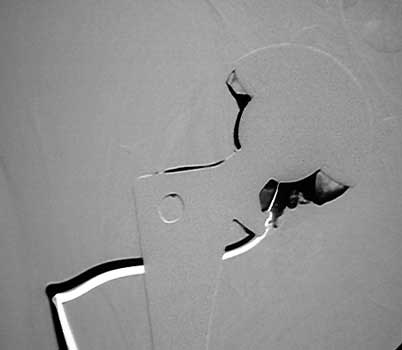 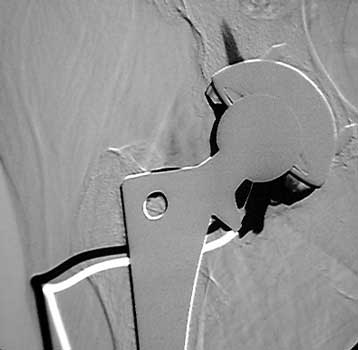 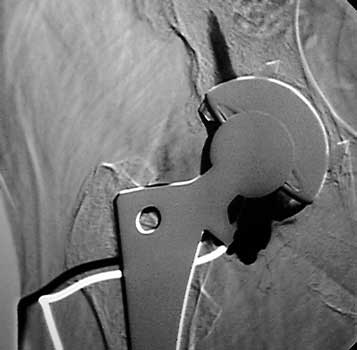
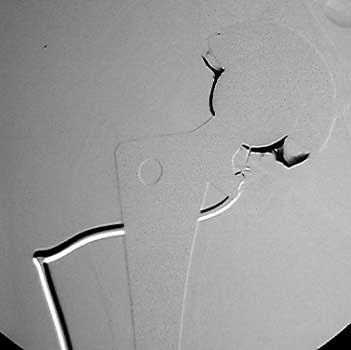
Normal arthrogram
Dry tap
DDx:
- Dry joint
- Large periarticular bursa acting as sump for fluid
- Sinus track allowing for continuous drainage of joint
- Non bacteriostatic saline wash performed
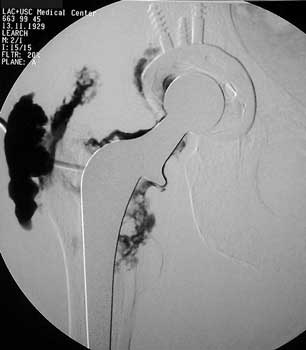 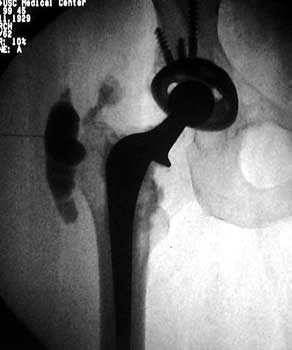
Dry tap secondary to large greater trochanteric bursa, 20
gauge spinal needle placed in bursa under fluoroscopic guidance
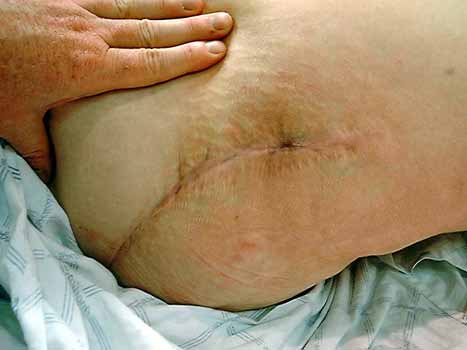
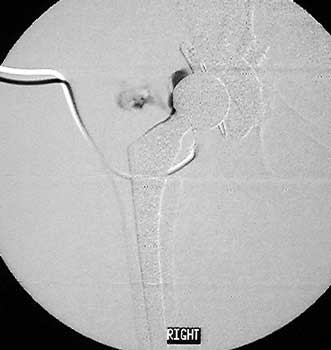 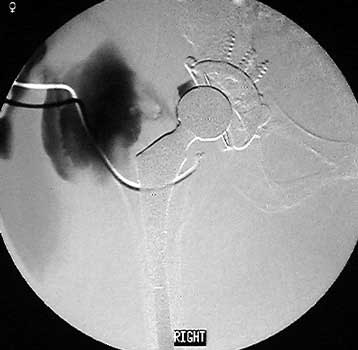 
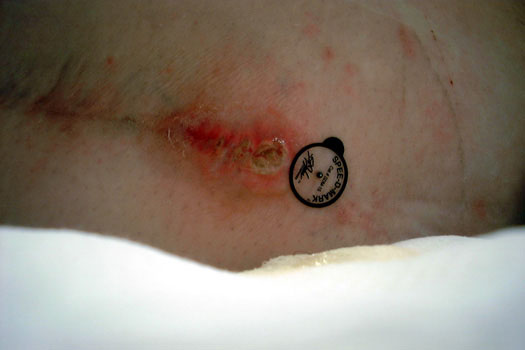
Scar with focal area of drainage. Dry tap secondary to large greater trochanteric bursa with
sinus tract draining to skin
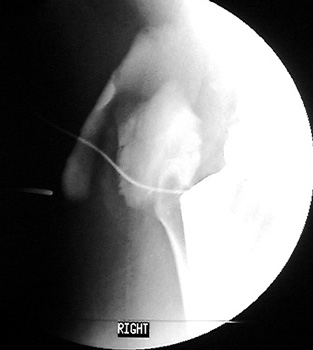
Dry tap secondary to sinus tract decompression
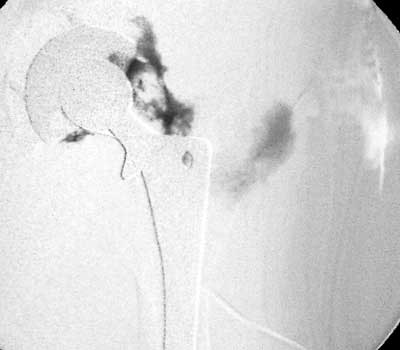 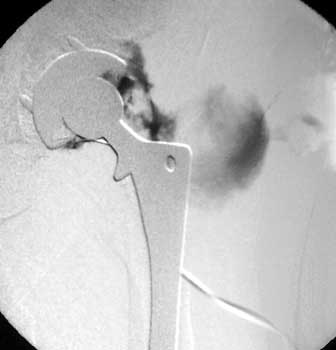 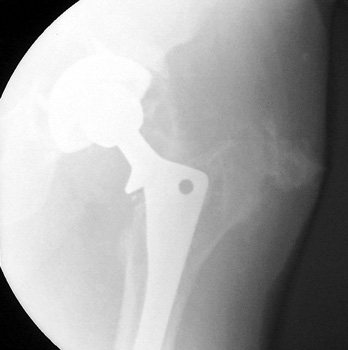
Dry tap secondary to sinus tract decompression
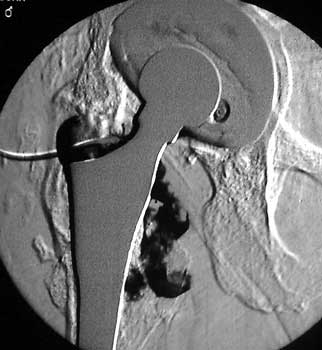 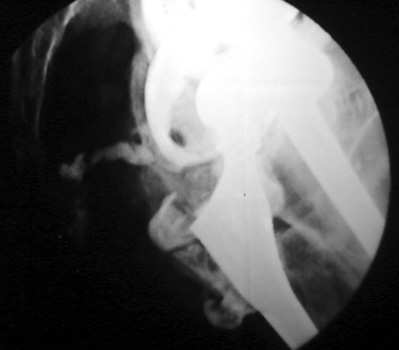
Sinus tract draining posteriorly
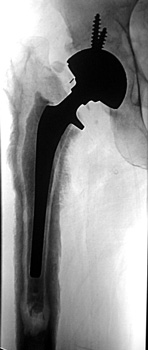 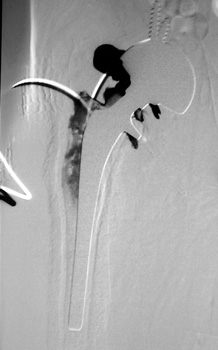
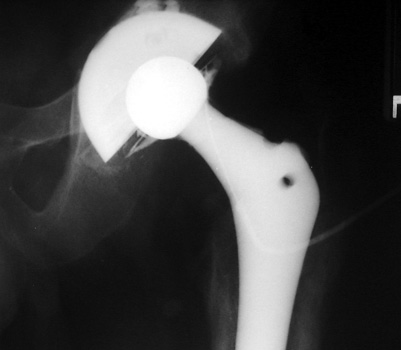
Arthrographic evidence of loosening—contrast enters
abnormally widened interface Gruen zone 1 and 2
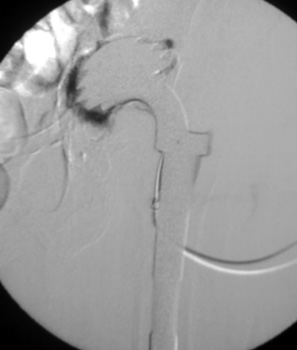
Arthrographic evidence of cup loosening—contrast enters
abnormally widened interface Gruen zone II and III
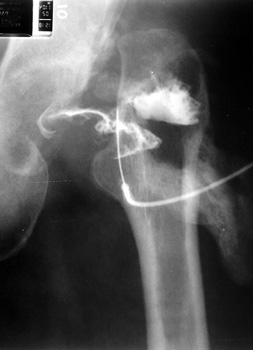
Aspiration of hip after removal of prosthesis. Needle placed
at femoral edge where fluid collects. Needle should not be placed in acetabular
area, which may not be fully intact, risking needle entry into pelvic cavity.
|